Whether navigating drones over vast agricultural landscapes or guiding survey robots through intricate urban environments, the accuracy provided by RTK-enabled devices is unmatched.
In the realm of precision location and navigation, RTK (real-time kinematic positioning) has emerged as an indispensable technology, revolutionizing our ability to navigate with unparalleled accuracy.
In this guide, we’ll take a deep dive into the world of RTK networks, exploring what RTK is, how RTK networks work, and how to choose the right RTK network for your location precision needs.
What is an RTK network?
RTK positioning is a precise satellite navigation technique used to enhance the accuracy of position data obtained from GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) receivers. By comparing the phase difference between the signals received from satellites and those from a fixed base station, RTK provides GNSS corrections that allow for centimeter-level accuracy in real time.
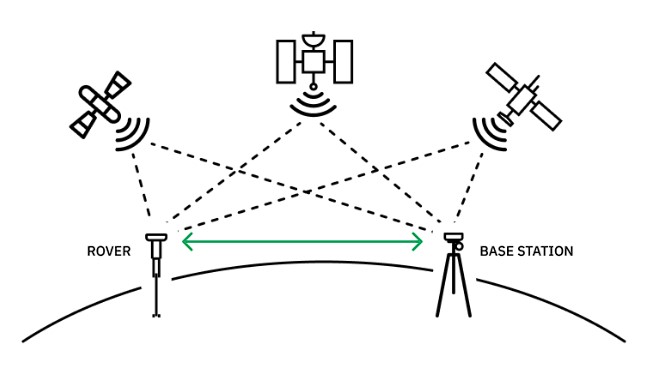
An RTK network expands upon the traditional RTK setup by incorporating multiple base stations interconnected within a network infrastructure. The base stations work collaboratively to provide correctional data to users across a wide geographical area.
The interconnectedness of an RTK network, which communicates across multiple base stations as well as with compatible receivers, allows for seamless handoff of correctional data between base stations. This ensures consistent accuracy and coverage over larger areas than would ever be possible with a single base station.
RTK Network vs Network RTK
Although RTK network and network RTK are often terms used interchangeably, there are differences in the fundamental architectures and operational mechanisms.
In an RTK network, each base station operates independently, continuously transmitting correctional data to nearby rover receivers. The rover receivers utilize the correctional data, along with signals received from satellites, to calculate their positions in real time.
The network architecture enables users to achieve precise navigation over large geographic areas, even in challenging environments with obstructed satellite visibility.
Network RTK, on the other hand, refers to a specific implementation of RTK technology where a single base station broadcasts correctional data to multiple rover receivers simultaneously. In this setup, the base station serves as a central reference point, continuously transmitting correctional data to receivers within its coverage area.
Network RTK allows multiple receivers to receive correctional data from the same base station, a centralized approach that simplifies the setup process and reduces the need for individual base stations.
While network RTK provides wide-area coverage, scalability, and cost-efficiency, it does have some drawbacks. An RTK network, due to the multiple base stations, can provide localized high-density coverage in dense urban environments or complex construction sites with significant obstructions, allowing for an accurate survey. The interconnected base stations provide precise corrections tailored to specific areas.
RTK networks also provide customization and control over correctional data transmission, making them suitable for applications with stringent accuracy requirements or specialized operational needs. Finally, the redundancy and reliability of an RTK network with interconnected base stations can mitigate the impact of signal interruptions or base station failures.
RTK Network vs RTK Clusters
While RTK networks offer widespread coverage through interconnected base stations, RTK clusters consist of multiple base stations deployed near each other. These clusters are engineered to provide ultra-precise positioning accuracy in concentrated zones where high-density coverage is essential.
Still, while base stations in an RTK cluster are nearby, they are not interconnected in the way an RTK network provides. Furthermore, the base stations in an RTK network may be strategically positioned across a larger geographic area.
These base stations can collaborate to provide correctional data to users, providing much more widespread coverage. The seamless connectivity, widespread coverage, and flexibility in deployment make RTK networks an optimal choice for many applications that require widespread coverage, such as agriculture and farm mapping.
How RTK Networks Work
RTK positioning technology relies on communication between the user’s rover and the RTK provider’s base station and some very important calculations. Let’s see how it works.
RTK Network Base Stations
Base stations serve as the backbone of RTK networks. These base stations are strategically positioned across a geographic area to ensure optimal coverage and accuracy. They are surveyed very precisely so that its position is known to within one or two centimeters.
Each base station continuously receives signals from satellites in the GNSS constellation and collects data on atmospheric conditions, satellite positions, and other factors affecting positioning accuracy. The base stations then transmit the data to compatible receivers in real time.
RTK-Enabled Receivers
An RTK-enabled receiver, often a rover, is equipped with a very heavy math routine that’s able to resolve the ambiguities in the carrier measurements. These GNSS corrections can compensate for errors introduced by factors such as atmospheric conditions, satellite orbit deviations, and signal propagation delays.
This unlocks the use of the previously unusable carrier phase and enables position determination to within a couple centimeters. By comparing the measurements the rover receiver makes to those obtained from the base station, the receiver can cancel out all the major sources of error in its own measurements. The resulting measurements are 100x more precise than normal stand-alone measurements.
RTK Network Access
It’s important not to think of RTK base stations as standalone units, but rather as pieces of broader, interconnected networks that together offer more expansive coverage. Since most organizations simply aren’t equipped to set up their own RTK or NTRIP system, RTK service providers use a complex network of base stations to broadcast correction data essential for high-precision tasks in surveying, construction, and automated systems.
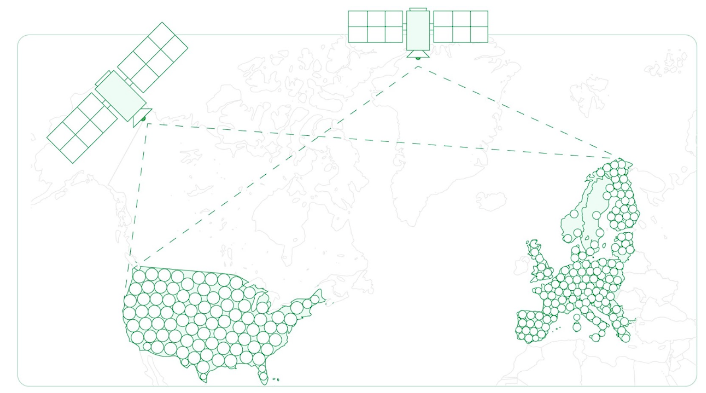
For example, Point One’s Polaris RTK network has global coverage across the US, EU, UK, CA, and AU and boasts the highest overall density of US RTK corrections networks. This allows the network to offer scalable solutions and ensure high accuracy–even in areas without cellular coverage or in challenging environments in urban canyons.
Benefits of RTK Networks
RTK networks offer several compelling benefits that revolutionize precision navigation and surveying processes. Let’s explore some of these advantages.
Dense Coverage
RTK networks provide extensive coverage through the network of interconnected base stations. Unlike traditional setups where users rely on a single base station, RTK networks leverage multiple base stations working collaboratively to ensure comprehensive coverage.
This dense network infrastructure minimizes signal obstructions and enhances accuracy, even in challenging environments.
Real-time, Accurate Corrections
One of the key advantages of an RTK network is its ability to deliver real-time, accurate corrections to users’ positioning data. RTK networks account for errors in positioning in real-time, continuously broadcasting correction information from the fixed base stations to the rovers.
As a result, users can achieve immediate centimeter-level accuracy in their navigation and surveying tasks. This enables users to make informed decisions and execute tasks with precision, thereby enhancing efficiency and productivity.
Base Station Management
In traditional RTK Setups, users are responsible for deploying and managing their own base stations, which can be complex and resource-intensive. When factoring in overhead costs, downtime, maintenance, and corrections, building your own RTK may not be the best solution.
Using an RTK network simplifies this process by providing a network of base stations managed by a service provider. Users no longer need to invest in their own base station infrastructure or worry about maintenance or calibration–all of which are incredibly complex, expensive, and time-consuming.
Instead, they can simply connect their devices to the existing RTK network, allowing them to focus on their core tasks without unnecessary overhead and expenses.
Security
RTK network systems often incorporate robust security measures to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches. By leveraging encrypted communication protocols and authentication mechanisms, RTK network providers ensure the integrity and confidentiality of correctional data transmitted between base stations and receivers.
The enhanced security of an RTK network safeguards sensitive information and prevents malicious actors from tampering with positioning data.
Scalability
RTK networks offer scalability advantages, allowing the infrastructure to expand and adapt to evolving user requirements and coverage needs. As user demand grows or new geographic areas require coverage, RTK network providers can deploy additional base stations and expand the network’s reach accordingly.
For example, Polaris grows based on client requests. With 1,400 base stations and counting, Point One will grow where you need and get the systems up and running for you.
Cost Efficiency
RTK networks present a cost-effective solution compared to traditional RTK setups, particularly for users who require widespread coverage or operate in multiple locations. Instead of investing in and maintaining their own base station infrastructure, users can leverage the network of base stations provided by the service provider through a subscription model.
This eliminates upfront capital expenditures and ongoing maintenance costs associated with base station ownership.
Public RTK Networks vs Private RTK Networks
When considering RTK networks, the choice between public and private options can significantly impact the performance and reliability of your positioning data. Let’s explore a few key considerations.
Accuracy
While Public RTK networks often boast extensive coverage and access to a wide array of base stations, they tend to be less accurate than private networks.
Private RTK networks offer a more tailored approach to accuracy. By deploying dedicated base stations and control over network configurations, private networks can be optimized for specific use cases or industries.
This customization enables users to fine-tune network parameters to meet their unique accuracy requirements, whether for precision agriculture, construction, or surveying applications.
While private networks may offer slightly less coverage than public networks, they excel in delivering unparalleled accuracy. These providers offer features that ensure active and reliable positioning and are crucial in industries and communities where precision is non-negotiable.
Uptime
When something goes wrong with a public RTK network, you might be looking at some serious downtime. For businesses that need to provide complete, comprehensive location accuracy, using a public RTK network is a risk.
Private RTK networks prioritize uptime to meet the demands of users with stringent operational requirements. By maintaining control over network infrastructure and monitoring systems, private network operators can go beyond the capabilities of public networks by quickly managing any issues that occur.
Customer Support
Since public RTK networks often don’t have a team dedicated to customer support, technical issues, network access, and troubleshooting can be a major challenge.
Private RTK networks are better equipped to prioritize personalized customer support tailored to users’ needs. With direct access to network operators and technical experts, users can receive prompt assistance with their specific issues.
How to Choose the Best RTK Network
Before selecting the best RTK network for your precision location needs, you’ll want to consider several key factors.
Accuracy
Accuracy is paramount when choosing an RTK network, particularly for applications that demand precise positioning data. Evaluate the network’s track record and reputation for delivering centimeter-level accuracy in various operating conditions and environments.
Look for networks that offer robust correctional algorithms and quality assurance measures to ensure consistent accuracy across your desired operating area.
Number of Base Stations
The number of base stations within an RTK network directly impacts coverage and reliability. Opt for networks with a sufficient density of base stations to provide seamless coverage across your intended operating area.
Consider the distribution of base stations and their proximity to your work sites to ensure optimal performance and accuracy, especially in challenging terrain or urban environments. Fortunately, Point One has one of the densest networks in the world with 1400+ base stations worldwide, and continues expansion driven by customer demand.
Uptime
Uptime is critical for uninterrupted access to correctional data and reliable positioning results. Assess the network’s uptime track record and infrastructure reliability, including backup systems and failover mechanisms. Look for networks with high availability and proactive maintenance practices to minimize downtime and ensure continuous operation, even under adverse conditions.
The reliability of private RTK networks can be seen with Point One Polaris, which boasts a 99.99% uptime.
Coverage
Coverage breadth and depth are essential considerations when choosing an RTK network. Evaluate the network’s geographic coverage and assess whether it aligns with your operational requirements and geographic scope.
Consider factors such as regional coverage limitations, signal obstructions, and network expansion plans to ensure comprehensive coverage across your desired operating area. With Point One Polaris, even in areas without cellular coverage, Polaris provides high-accuracy GNSS corrections with delivery over satellite.
Navigation Constellation & Frequency Support
Compatibility with various navigation constellations (e.g., GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, BeiDou) and frequency support are crucial for flexibility and interoperability. Verify that the RTK network supports the GNSS constellations and frequencies relevant to your region and application.
Additionally, consider networks with multi-constellation support and frequency diversity to enhance resilience and accuracy in challenging environments. Point One Polaris’ precision location stack utilizes multiple frequencies to improve accuracy.
Integration Options
Integration capabilities play a vital role in streamlining workflows and maximizing efficiency. Evaluate the network’s compatibility with your existing hardware, software, and data formats to ensure seamless integration into your operational ecosystem.
Look for networks with open APIs, standard protocols, and compatibility with popular GNSS receivers and software solutions to facilitate interoperability and ease of implementation. Point One makes it easy to quickly build production-grade products that operate safely and reliably in the physical world — offering maximum flexibility and integration.
RTK Network Cost
Cost considerations encompass both initial investment and ongoing subscription or usage fees. Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including hardware, software, subscription fees, and any additional services or support.
Fortunately, with Polaris, Point One has developed a cost-effective, state-of-the-art solution, allowing you to subscribe to a trustworthy RTK network.
Polaris offers several transparent pricing subscription options. For less than half the cost of legacy RTK networks, Polaris offers accuracy 100x greater than GNSS within minutes of setup. With 99.99% uptime and over 1400 base stations, Polaris allows you to subscribe to one of the densest RTK networks in the world.
More About RTK Networks
Now that we’ve covered the ins and outs of RTK networks, let’s return to some of the most common questions and misconceptions surrounding this groundbreaking technology.
What is the difference between GPS and RTK?
GPS (Global Positioning System) is a satellite-based navigation system that provides location and time information to users anywhere on or near Earth. While GPS offers accuracy within several meters, RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) is a precise satellite navigation technique that enhances GPS accuracy to centimeter-level precision in real time.
In short, RTK provides groundbreaking enhancements to GPS location precision.
Does RTK need internet?
RTK doesn’t necessarily require internet connectivity to function. RTK relies on communication between a base station and a rover receiver to transmit correctional data in real time.
This communication can occur via radio frequency (RF) signals, cellular networks, or other wireless communication methods, depending on the RTK system’s configuration and user preferences. While internet connectivity is often used for RTK services, it’s not a fundamental requirement for RTK operation in all scenarios.
RTK Network Map
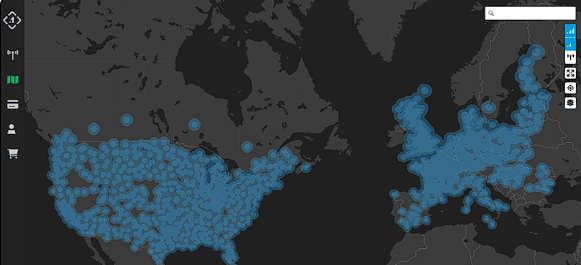
An RTK network map provides a visual representation of the coverage area and distribution of base stations within an RTK network. This map typically displays the location of base stations, their respective coverage areas, and other relevant information such as signal quality and availability.
RTK network maps are valuable tools for users to assess network coverage, plan field operations, and optimize positioning accuracy. By consulting an RTK network map, users can identify nearby base stations, evaluate coverage overlap, and determine the most suitable stations for their specific application or location.
Take, for example, the map above of Point One’s 1400+ base stations, which span multiple continents for maximum coverage.
Access the Best RTK Network
Accessing the best RTK network is essential for achieving optimal precision and reliability in your navigation and surveying endeavors. By considering factors such as accuracy, coverage, uptime, integration options, and cost, you can select an RTK network that aligns with your specific requirements and operational objectives.
For those seeking a top-tier RTK network solution, look no further than Point One Polaris, a premier provider of precision positioning services. With its state-of-the-art infrastructure, industry-leading accuracy, extensive coverage, and seamless integration options, Point One Polaris offers a comprehensive solution for precision navigation, surveying, and location-based applications.
To access the best RTK network and unlock unparalleled precision and reliability, visit Point One Polaris today. Unlock the full potential of precision positioning with Point One Polaris — your trusted partner for superior RTK network solutions.
