Farm mapping and agricultural mapping are changing how we farm, leading us into a new era of agricultural technology. These methods are crucial for precision agriculture, preparing the ground for smarter farm management and the rise of farm robots.
Companies like Monarch Tractor and Burro are leading the charge, with Burro recently securing $24 million in funding to grow their agricultural robot technology. This year marks a turning point, where we expect to see the real growth of robotics and automation in farming, reshaping how we approach agriculture.
This guide explores the essentials of farm and agriculture mapping, highlighting how they streamline farm operations, from crop health monitoring to resource management. We’ll also examine how precision location tools like Point One Polaris are pivotal in elevating these practices, offering farmers the precise, actionable data needed for smarter, more sustainable farming.
Farm mapping vs agriculture mapping vs field mapping
Understanding the distinctions and similarities between farm mapping, agriculture mapping, and field mapping is key to leveraging these tools effectively in precision farming.
- Farm Mapping: Farm mapping broadly covers the creation of detailed maps for entire farming operations. It includes layouts of fields, buildings, livestock areas, and even infrastructure like irrigation systems. Farm mapping helps farmers manage their land more effectively, plan rotations, and organize resources.
- Agriculture Mapping: Agriculture mapping focuses more on the cultivation aspects of farming. It involves a detailed analysis of crop areas, including soil composition, crop health, and yield data. This type of mapping is vital for making informed decisions about planting, fertilizing, and harvesting.
- Field Mapping: Field mapping zooms in further, concentrating on individual fields or specific areas within a farm. It’s often used for more detailed tasks like soil zoning, spot spraying, and precision planting. Field mapping is essential for operations that require higher frequency and detailed attention, such as managing grazing patterns or targeted pest control.
Advantages of precision farm mapping
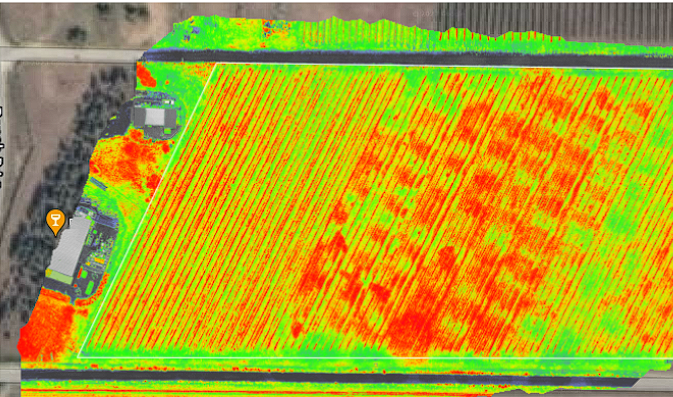
Precision farm mapping is not just about plotting land; it’s a strategic approach that elevates every aspect of modern farming.
Improve Farming Efficiencies
Precision farm mapping allows farmers to visualize and analyze their fields with exceptional detail. This clarity leads to more informed decisions, optimizing planting, irrigation, and harvesting tasks.
Farmers minimize waste and maximize the productivity of every acre by knowing exactly where to allocate resources.
Reduce Cost
Accurate farm maps help pinpoint areas of waste and inefficiency. Whether identifying underperforming sections or optimizing resource use, the data from precision mapping directly contributes to cost savings.
This efficiency is not just about reducing expenses but also about enhancing the overall yield and quality of produce.
Easier Land Management
Modern farm management is complex, involving numerous variables from crop rotation to pest control. Precision mapping simplifies these tasks by providing a clear overview of the farm’s layout and condition.
This information is vital for planning, whether it’s for short-term operations or long-term development strategies.
Sustainable Practices
Precision farm mapping is even more crucial with the growing emphasis on sustainable agriculture. It supports practices that protect the environment, such as targeted pesticide application and efficient water usage, contributing to more eco-friendly farming.
How does agriculture mapping work?

Agriculture mapping blends sophisticated tools and methods to give farmers detailed insights into their land. This integration of technology in farming practices not only improves crop management but also paves the way for innovative agricultural solutions.
RTK Network
RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) technology, offered by NTRIP service providers, revolutionizes farm mapping by providing real-time GNSS corrections to GPS data. This enables pinpoint accuracy for locating elements like crop rows, irrigation systems, and land boundaries and significantly reduces the time spent on processing.
Typically, photogrammetry requires extensive processing to stitch together various images into a coherent map. However, with RTK, the technology’s precise location and data act as an initial reference point, dramatically speeding up this process.
Point One Polaris utilizes a network of precisely located base stations to offer centimeter-level accuracy, a key factor in creating highly detailed and reliable farm maps. This accuracy isn’t just about precision; it’s a catalyst for time efficiency in farm planning and operations. By cutting down the time needed for photogrammetry, farmers can focus more on productive tasks.
Read more about how to use RTK for accurate mapping
Agriculture Drones
Drones, especially those equipped with RTK technology, play a pivotal role in modern agriculture mapping.
- Detection: Equipped with advanced sensors, agriculture drones fly over fields, collecting data on crop health, soil condition, and hydration levels. This information is vital for identifying issues like disease or under-watering, enabling farmers to take swift, targeted action.
- Action: Beyond detection, ground-based drones (robots or rovers) are increasingly used in direct farming actions like fertilization, pest control, and even automated harvesting. These drones carry out precise operations based on collected data, optimizing resource application and improving crop yield.
Farm Mapping Software
Farmers use sophisticated farm mapping software to process and make sense of the data collected by RTK networks and drones. Tools like GIS (Geographic Information Systems) analyze this data, translating it into actionable insights.
This software lets farmers visualize their land in various layers, making informed decisions about crop placement, irrigation schedules, and more.
Agriculture Mapping Use Cases

Today’s agriculture mapping goes beyond basic land measurement, playing a crucial role in various aspects of modern farming.
Path Planning
Agriculture mapping provides detailed data for programming autonomous agricultural vehicles and equipment. Whether navigating between crop rows or covering specific field areas, the precision offered by advanced mapping ensures the efficient and effective operation of autonomous farming systems.
Crop Health & Yield
By analyzing data collected from various sources, including satellites and drones, farmers can detect issues like disease or nutrient deficiencies early on. This proactive approach allows for timely interventions, enhancing crop health and maximizing yield.
Agriculture Robotics
Innovations like fruit-picking robots and automated harvesters rely heavily on accurate agriculture maps. These maps guide robotics in performing complex tasks across vast farmlands, ensuring accuracy and reducing manual labor requirements.
Variable Rate Applications
Variable rate technology (VRT) uses agriculture mapping to apply inputs like fertilizers and pesticides in precise quantities. This method reduces waste, lowers costs, and minimizes environmental impact, contributing to more sustainable farming practices.
Prescription Maps
Prescription maps, created through detailed agriculture mapping, guide farmers on where and how to apply resources. These maps ensure optimal resource use for different parts of a field, catering to the unique needs of each area and enhancing overall farm productivity.
Farm Planning
Effective farm planning relies on accurate maps to strategize land use, crop rotations, and resource allocation. Farmers gain a comprehensive view of their land with agriculture mapping, facilitating smarter, data-driven decisions that optimize available resources.
Spot Spraying
Agriculture mapping aids in identifying specific areas that require treatments like pest control or weed spraying. Spot spraying, guided by precise maps, targets only the areas in need, enhancing efficiency and reducing chemical usage.
Boundary & Obstacle Mapping
Farm mapping helps accurately define property boundaries and identify potential obstacles in the field. This information is crucial for legal purposes and in planning the layout and movement of farm machinery.
Soil Zoning
Soil zoning maps, derived from agriculture mapping, indicate variations in soil properties across a farm. This information guides farmers in tailoring cultivation practices to suit different soil zones, leading to better crop growth and soil management.
More About Agriculture & Farm Mapping

Diving deeper into the specifics of agriculture and farm mapping reveals how these practices are pivotal in the evolution of modern farming.
What is map farming vs sensor farming?
Map farming involves creating detailed visual representations of farmland, focusing on field boundaries, crop distribution, and topography. On the other hand, sensor farming utilizes various sensors to gather real-time data on soil conditions, plant health, and environmental factors.
Both approaches complement each other, with map farming providing a macro view and sensor farming offering micro-level details.
How do farmers use GPS on farms?
GPS technology in farms is used for many purposes, from guiding tractors and machinery to precise locations to monitoring crop health and soil conditions. With RTK GPS, farmers can implement precision agriculture techniques, ensuring resources are utilized optimally, and crops are managed effectively.
What are field navigators?
Field navigators are advanced GPS systems used in farming to assist with navigation across large agricultural fields. They help accurately map and plot courses for machinery, ensuring that tasks like planting, fertilizing, and harvesting are done with precision.
What is a farm sprayer GPS?
A farm sprayer GPS enables precise application of fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides. Using GPS to guide the spraying process, farmers can ensure that these substances are applied evenly and only where needed, reducing waste and environmental impact.
What is the field area measure GPS?
GPS field area measure tools are used by farmers to calculate the size of their fields accurately. This information is vital for planning purposes, such as calculating seed and fertilizer requirements and optimizing irrigation systems.
What is the best field mapping app?
The best field mapping apps offer user-friendly interfaces and comprehensive features, enabling farmers to create, view, and manage detailed maps of their fields. These apps often integrate with other agricultural technologies for a seamless farming experience.
What is the best drone for farm mapping?
The best drones for farm mapping are equipped with advanced sensors and cameras, capable of capturing high-resolution images and data. These drones provide farmers with an aerial perspective, essential for detailed mapping and analysis of crop health, soil moisture, and more.
What is navigation in agriculture?
Navigation in agriculture has evolved significantly with the adoption of GPS and RTK technologies. These tools enhance the accuracy of farm machinery, guiding them along precise paths and ensuring optimal use of resources.
Navigation technology reduces application overlap, saves time, and minimizes environmental impact.
Improve Your Farm Mapping Precision
Advancements in farm mapping technology have opened new avenues for enhancing agricultural practices. Precision mapping is key to unlocking the full potential of modern farming, from detailed land analysis to efficient resource management.
For farmers and agricultural professionals seeking to refine their mapping precision, Point One Polaris offers an unmatched solution. Its advanced RTK network gives it the accuracy and reliability essential for modern farm mapping.
Whether for detailed soil analysis, efficient path planning for autonomous equipment, or precise application of farm inputs, Point One’s technology ensures that your mapping data is accurate and actionable. You access cm-accurate positioning on your hardware–with lightning-fast convergence times of less than five seconds on the RTK network.
Contact a specialist today to discover how Point One Polaris can transform your farm mapping and agricultural practices.
