Polaris RTK Corrections Network
Affordable, global precision without the hassle
Unparalleled GNSS accuracy. Get cm-accurate positioning on your hardware with lighting fast convergence times (<5s) on our RTK Corrections Network.
1400+
RTK Base Stations
> 386K
RTK Correction Devices
99.99%
RTK Network Uptime
< 5s
Network Convergence Time
Unparalleled RTK Accuracy and Reliability
Built from the ground up for cm-accurate GNSS positioning, at 99.99% reliability.
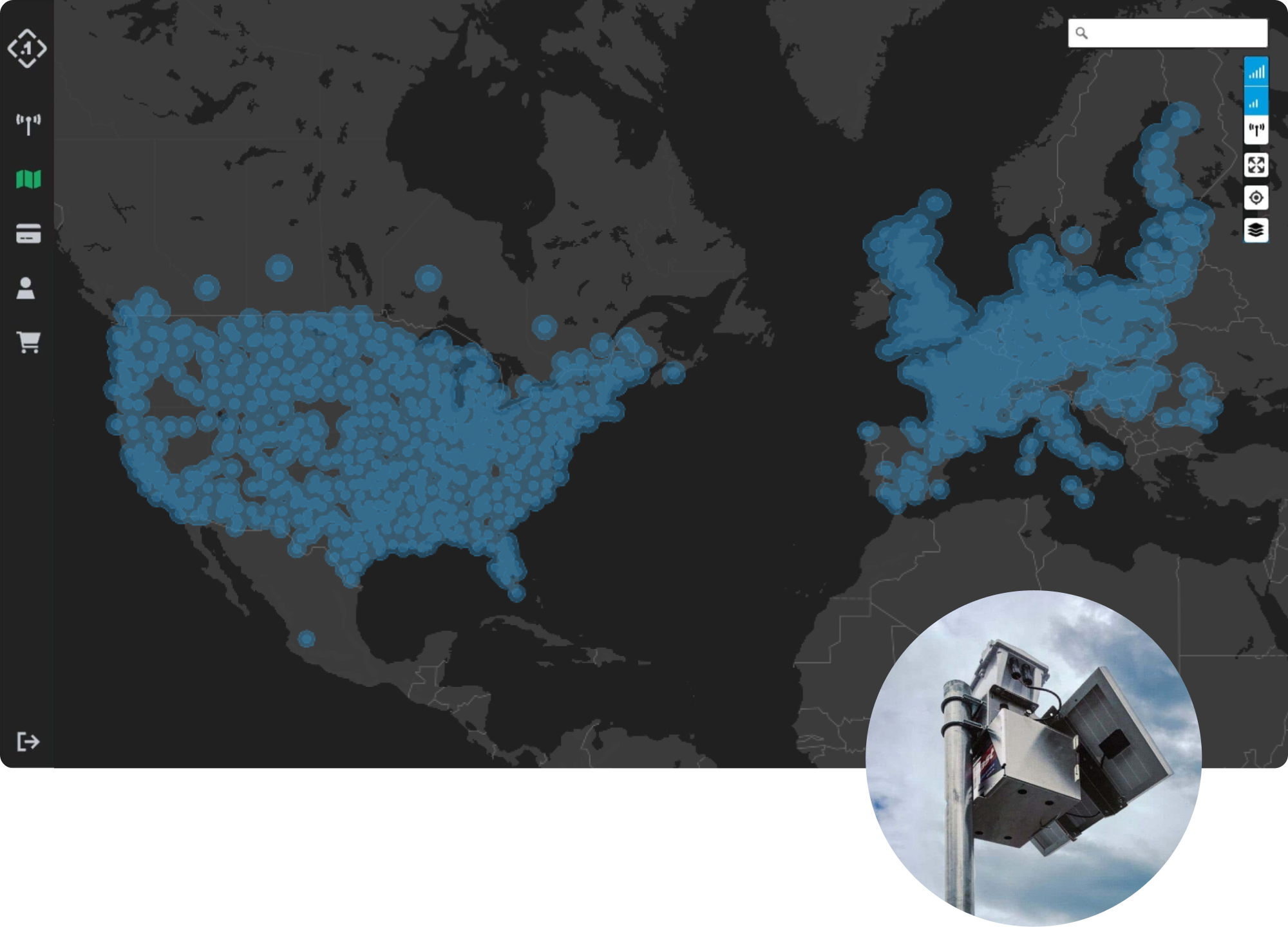
RTK Corrections Data Where You Need It
The Polaris RTK network has global coverage across the US, EU, UK, CA and AU. Get global RTK corrections from a single mountpoint.
Easy to Set Up On Your Hardware
Setup in 5 minutes by connecting to a single NTRIP mount point.
A dense global network of RTK base stations
- Highest overall density of U.S. RTK corrections networks
- Extra RTK base station redundancy in urban centers (top 50 cities in the US all have over 4 stations)
- Tracks four major constellations: GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, BeiDou
- Uses the ITRF 2014 current epoch coordinate reference system
- Easy-to-expand RTK network driven by customer demand
- Even in areas without cellular coverage, Polaris provides high accuracy GNSS corrections with delivery over satellite
- 99.99% uptime of the RTK corrections network
Explore our RTK network
More About
RTK Correction Networks
How is Point One different from standard GNSS?
Point One builds high precision GNSS solutions. Standard GNSS accuracy ranges from 1m to 10m and can be worse based on the operating environment. Point One’s high precision GNSS delivers accuracy from 10cm to 1cm, and does so even in challenging environments such as urban canyons and occluded sky-views
What is Precision GNSS?
How do I get started using Point One as a developer?
What products already integrate Point One?
What is RTK?
Can I use Polaris corrections with a non-Point One system?
Yes. The Polaris network performs as an RTK network. Non-Point One systems can access the Polaris network using standard NTRIP protocol. Access credentials and documentation are available at app.pointonenav.com.
What is the difference between Polaris and NTRIP corrections?
How do RTK corrections work?
RTK corrections account for various ambiguities present in navigation constellation signals, which can stem from sources such as satellite orbital errors and atmospheric disturbances. By sharing correctional data in real time, the fixed base station and rover together improve positional accuracy from meter-level to centimeter-level.
Let’s get a little more technical:
- Standalone GNSS positioning relies mostly on very accurate–but not very precise–pseudorange measurements of code phase. RTK relies on extremely precise– but ambiguous–RF carrier phase measurements.
- The heart of RTK is integer carrier phase ambiguity resolution. This process turns the ambiguous carrier phase measurements into highly precise measurements of pseudorange, which can be about 100x more precise than the code phase pseudorange measurements–but they are ambiguous to within an integer number of radio carrier wave cycles.
- An RTK-enabled receiver is equipped with a very heavy math routine that’s able to resolve the ambiguities in the carrier measurements. This unlocks the use of the previously unusable carrier phase and enables position determination to within a couple centimeters.
Fortunately, when using an RTK service like Point One Polaris, you don’t have to worry about any of this. You can get set up in five minutes by connecting to a single NTRIP mount point–and then access cm-accurate positioning lighting-fast convergence times.
What is an RTK base station?
An RTK base station is an integral part of any RTK positioning system. In order to correct errors in satellite signal data, RTK positioning requires stationary sites with known, precise locations to serve as reference points. These are called fixed base stations, which send observations to the rover in real time.
It’s important not to think of RTK base stations as standalone units, but rather as pieces of broader, interconnected networks that together offer more expansive coverage. For example, Point One’s Polaris RTK network has global coverage across the US, EU, UK, CA, and AU and boasts the highest overall density of US RTK corrections networks.
This allows the network to offer scalable solutions and ensure high accuracy, even in areas without cellular coverage or in challenging environments in urban canyons.
How accurate is RTK?
RTK offers unparalleled accuracy in positioning at centimeter-level precision. This high level of accuracy is essential for applications where even the slightest deviation can have significant consequences.
Point One’s RTK solutions are engineered to deliver exceptional precision within a few centimeters. This level of accuracy is made possible by Point One’s advanced algorithms, Polaris Network infrastructure, and commitment to using the latest technological advancements in GNSS corrections.
Point One’s RTK system is not just about precise measurements; it’s about providing reliable data you can trust for critical decision-making.
Which applications use RTK?
RTK technology is essential in many areas where exact positioning is needed. In farming, RTK helps guide machinery perfectly for planting and harvesting, boosting crop quality and farm efficiency. Robots in outdoor settings work better with RTK because it helps them navigate through the world with precision.
For preventing damage, especially during construction, RTK is vital for safely locating things like pipes and cables underground. Surveyors and mapmakers rely on RTK for precise measurements of land and buildings, which is important for planning new projects. In construction, RTK is key for correctly setting up sites and ensuring buildings are constructed accurately.
RTK is also crucial for self-driving cars to navigate safely, especially on busy streets. RTK is even changing how deliveries are made by helping to track and direct delivery vehicles, making sure packages get where they’re going on time.
What are GPS correction methods?
Several GPS correction methods, including RTK, PPP, and SSR, improve the accuracy of satellite-based positioning. Each method has its unique approach to correcting GNSS data.
RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) provides real-time corrections, offering centimeter-level accuracy. It’s ideal for applications needing immediate precision, such as autonomous vehicle navigation and precision agriculture. RTK works by comparing the signals from a network of fixed base stations to the satellite data, quickly correcting any discrepancies.
PPP (Precise Point Positioning), on the other hand, doesn’t use a network of base stations. Instead, it uses a single reference station and precise orbit and clock data to offer high accuracy. While PPP can achieve a somewhat similar level of precision to RTK, it takes much longer to converge, making it more suitable for applications where immediate accuracy isn’t critical.
SSR (State Space Representation) is a more advanced method that provides correctional data in a state space format. This technique models the GNSS errors, including satellite orbits and clocks, and atmospheric delays, offering high accuracy over large areas. However, many GNSS receivers aren’t equipped to effectively process all the data provided by SSR, making it difficult to convert into meaningful positions.
Note that discussing GPS, by itself, isn’t standard practice in RTK corrections. Today, unless specifically discussing the USA constellation system, we say “GNSS ” exclusively.
What is the range of RTK corrections?
RTK correction ranges vary depending on the use case. It’s challenging to put a definite number on this question, since many variables can affect accuracy, including how much of the sky is visible, the weather, and more.