RTK GPS, or Real-Time Kinematic Global Positioning Systems, represent a significant leap in geospatial positioning technology. Known for exceptional accuracy and real-time capabilities, Using RTK services for GPS is becoming a cornerstone in a wide range of applications, from precision agriculture to advanced robotics. With RTK and GPS, kinematic measurements have entered a new era of accuracy and efficiency, redefining what’s possible.
This article from Point One Navigation contains everything you need to know about RTK and GPS. It explores how RTK GPS works, its advantages over standard GPS, and the range of industries it supports. You’ll learn about the technology behind an RTK-GPS module, the role of fixed base reference stations in enhancing accuracy, and how RTK works with GPS re-broadcasts corrections to ensure precision in real-time positioning.
Whether you’re a geospatial technologies professional, a business looking to leverage RTK and GPS, or simply someone curious about this advanced technique used in modern positioning systems, understanding how using RTK with GPS is the first step towards appreciating its transformative impact.
What does RTK mean in GPS?
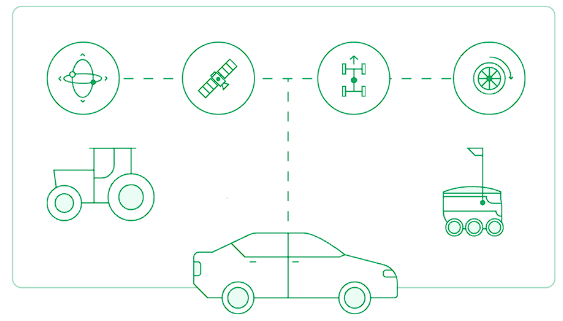
Using Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) with GPS is a highly advanced positioning technique in geospatial technologies. It improves the accuracy of standard GPS systems from meter-level to centimeter-level precision.
At its core, RTK works by using fixed base stations to provide real-time corrections for positional ambiguity inherent in GPS signals by transmitting them to receivers.
Base Station RTK
RTK base stations use a single, stationary reference station to broadcast corrections. This station knows its precise position and calculates error factors affecting GPS accuracy, like atmospheric interference and satellite clock errors.
The base station then sends these corrections to receivers, usually within a certain geographical radius. This method is highly effective for localized operations, but its accuracy diminishes as the distance from the base station increases.
RTK Network
In contrast to the single-station approach, an RTK network involves multiple RTK base stations, creating a larger area containing interconnected stations. This network approach ensures that the RTK corrections are more accurate over a wider area, making it ideal for operations that span larger regions.
RTK networks like Point One Polaris utilize certain frequencies and built-in UHF-band to efficiently transmit corrections to mobile units, enhancing the reliability and scalability of RTK and GPS technology.
Why You Need RTK with GPS
The need for RTK GPS in modern geospatial applications stems from the inherent inaccuracies in standard Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) technology.
GNSS inaccuracies arise from several factors. Signal delays caused by the Earth’s atmosphere, imprecision in satellite orbital data, and the limitations of satellite clock synchronization are some of the primary culprits. These factors can lead to unacceptable positional errors in professional, industrial, or scientific contexts where precision is paramount.
RTK addresses these issues by providing real-time corrections to GNSS data. It uses a network of fixed base stations that have a known, precise location. These stations monitor the errors in GNSS signals and broadcast correction information to the RTK receivers. This process significantly reduces GNSS errors, achieving positional accuracy down to the centimeter level.
The impact of RTK on GPS is significant across various fields. In agriculture, it enables precision farming, allowing for more efficient use of resources. In construction and surveying, it ensures that measurements and layouts are accurate, minimizing costly mistakes. For autonomous vehicles and robotics, RTK and GPS are essential for reliable navigation and operational safety.
RTK GPS transforms GNSS technology from one of approximate location to one of precision and reliability. This shift is not just a matter of improved accuracy; it’s about enabling new capabilities and applications in a world increasingly reliant on precise geospatial data.
How RTK and GPS Works
RTK is a sophisticated technique that enhances GPS data to achieve centimeter-level accuracy. It hinges on the interaction between several critical elements: GNSS inaccuracies, RTK receivers, and RTCM (Radio Technical Commission for Maritime Services) correction data.
1. GNSS Inaccuracies
GNSS systems, while globally operational, are subject to various inaccuracies due to atmospheric conditions, satellite clock errors, and ephemeris (satellite orbit) errors. These inaccuracies can lead to positioning errors, which are generally acceptable for everyday use but inadequate for tasks requiring high precision.
2. RTK GPS Receivers
The RTK GPS receiver is a specialized device that receives both the standard GNSS signals and the RTK correction data. Unlike traditional GPS receivers, RTK receivers can interpret the additional data to pinpoint their location with much greater accuracy.
3. RTCM Correction Data
The key to RTK’s precision lies in the RTCM correction data. This data is generated by a network of fixed base stations that continuously monitor GNSS signals. By comparing their known precise location with the location indicated by the GNSS signals, these stations calculate correction data.
This data, encapsulated in the RTCM format, is then broadcast to RTK receivers. Here are some of the options for receiving RTCM corrections:
- Dedicated RTK Networks: Operators can subscribe to dedicated RTK or NTRIP networks like Point One Polaris, which provide wide-area coverage and continuous RTCM data. These networks offer a hassle-free solution with operational reliability and are especially beneficial for users covering a larger area or requiring high mobility.
- Building Your Own Reference Station: For localized operations, setting up a personal GNSS reference station is an option. Unfortunately, setting up your own RTK system is time consuming, expensive, and requires serious technical expertise.
- Publicly Available Stations: Some organizations offer RTCM data through public stations. While this could be cost-effective, availability and coverage can be variable and rather limited.
Features of RTK GPS Systems
RTK GPS technology has an array of sophisticated features that significantly improve geospatial positioning and accuracy. These features not only set RTK-powered GPS apart from traditional GPS systems but also make it an indispensable tool in numerous applications where location precision is critical.
Convergence Time
RTK is notable for its quick convergence time. This term refers to the time taken for the system to achieve its full accuracy after being switched on. The short convergence time of RTK means it can start providing precise data much faster than traditional systems.
Coverage Density
A crucial factor for the effectiveness of RTK GPS capabilities is the density of its network coverage. Providers like Point One Navigation offer extensive coverage with a dense network of base stations, ensuring reliable and accurate positioning across large areas.
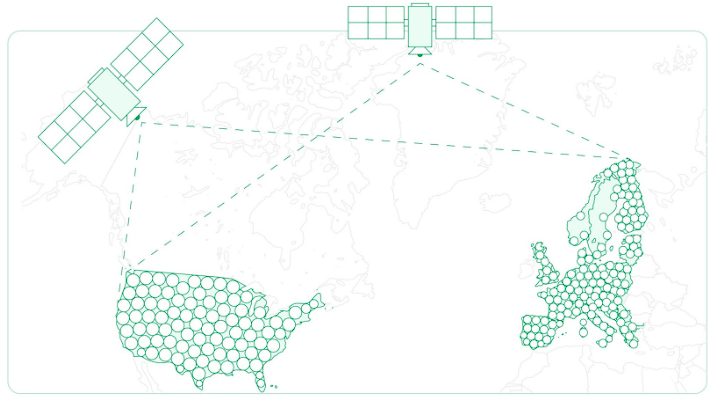
Real-time Data
Unlike Post-Processed Kinematic (PPK) systems, where it’s recommended to wait at least 24 before post-processing data, RTK provides real-time correction data. This feature is crucial for applications that require immediate and precise location information, such as autonomous vehicle navigation or machine control.
Positional Accuracy
The core benefit of pairing RTK with GPS is its exceptional positional accuracy. By correcting the common inaccuracies associated with GNSS signals, RTK GPS can pinpoint locations to within centimeters, a significant improvement over the meter-level accuracy of standard GPS.
Accessible UI
The user interface (UI) of RTK-GPS systems is designed for accessibility. An intuitive UI ensures that users can effectively manage and interpret the high-precision data that RTK provides.
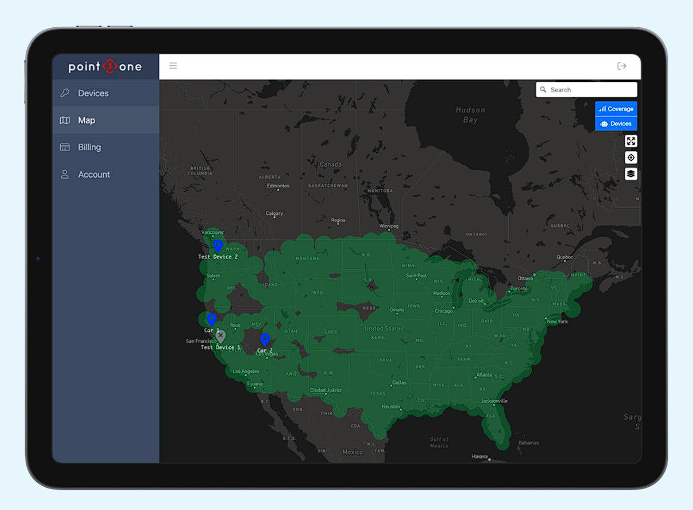
PointOne Dashboard
Reliability
Operational reliability is a key attribute of RTK-GPS systems. It consistently delivers high accuracy under various conditions, making it dependable for critical applications in sectors like construction, surveying, and agriculture.
API Availability
Many RTK-GPS systems, including those offered by Point One Navigation, come with an accessible Application Programming Interface (API). This allows for easy integration of RTK and GPS data into various software applications, improving its utility and flexibility.
Point One’s GraphQL API provides instant integration and centimeter-accuracy for GNSS-powered devices–while skipping REST API complexities, the hassle of learning multiple endpoints and data models, and setting up infrastructure for intermediate data stores and applications.
Provisioning
RTK GPS systems often feature user-friendly provisioning, meaning they can be set up and configured with minimal hassle. This ease of setup is necessary for users who may not have specialized technical knowledge.
Applications of RTK for GPS
RTK technology has revolutionized numerous fields, offering precise, real-time positioning critical for many modern applications. From agriculture to autonomous vehicles, the range of its use is a testament to its versatility and effectiveness.
Agriculture
In agriculture, RTK-GPS systems are instrumental for tasks like crop mapping, field surveying, and tractor automation. It enables farmers to implement precision farming techniques, leading to optimized resource usage, increased yields, and reduced environmental impact.
Robotics
Using RTK for GPS enhances the capabilities of robotic systems, particularly in autonomous navigation. It ensures precise positioning and path planning, valuable for applications like drone mapping, automated surveying, and robotic field operations.
Damage Prevention
In industries like utility and infrastructure, RTK helps accurately locate underground assets, thus preventing damage during excavation and construction activities.
Mapping & Surveys
For surveyors and mappers, RTK provides the high level of accuracy required for topographic surveys, GIS (geographical information system) data collection, and large-scale mapping projects.
Construction
In construction, RTK GPS is used for site layout, machine control, and monitoring structural movements. Its precision improves construction efficiency, safety, and compliance with design plans.
Autonomous Vehicles
RTK data systems are crucial for the navigation systems of autonomous vehicles, providing the accuracy and reliability needed for safe and efficient operation.
Delivery Logistics
RTK GPS plays a significant role in optimizing delivery logistics, aiding in route planning and fleet management for timely and accurate deliveries.
Learn More About RTK and GPS Solutions
RTK with GPS has redefined what’s possible in terms of accuracy and operational efficiency. From optimizing farming practices to enabling the safe navigation of autonomous vehicles, RTK and GPS are at the forefront of innovation. Its importance in various fields is a reflection of its reliability, precision, and versatility.
As technology continues to advance, the capabilities and applications of RTK GPS are primed for further expansion, offering new solutions to complex challenges.
For anyone looking to understand how this technology can benefit their specific needs or how to integrate RTK into their GPS operations, Point One Navigation offers expert insights and solutions. With advanced RTK technology, Point One Nav is dedicated to providing high-quality, reliable, and accessible positioning solutions.
Discover how RTK can transform your operations and projects. Whether you’re in agriculture, construction, surveying, or any field requiring precise geospatial data, Point One Navigation has the expertise and technology to elevate your work.
Contact a Point One expert today to learn more about RTK-GPS solutions and how they can be tailored to your needs.
